Java Tutorial
IntroductionEnvironment SetupIDEBuild ManagementLanguage SpecificationBasic ProgramVariablesData TypesPackagesModifiersConditionalsLoopsObject OrientedClassesSuperInterfacesEnumStatic importInheritanceAbstractionEncapsulationPolymorphismBoxing & UnboxingConversion Formatting numbers Arrays Command line arguments in java Variable Number of arguments in Java Exception handling in Java String handling in Java StringBuffer and StringBuilder in Java Mathematical Operations in Java Date and Time in Java Regular expressions in Java Input output programming in Java File Handling Nested Classes Collections Generics Serialization Socket programming Multi-Threading Annotations Lambda Expressions Reflections in Java Singleton class in Java Runtime Class in JavaHow to load resource in JavaHow to load properties file in JavaAdvanced
Log4j – Logging framework in JavaInterview Questions in JavaEncapsulation means hiding the implementation details from the outside world. Below image shows how encapsulation is achieved in Java by declaring the private members of the class. Remember that We can not access the private members from outside of the class. Thus, any changes made inside the class with respect to private members do not impact outside classes.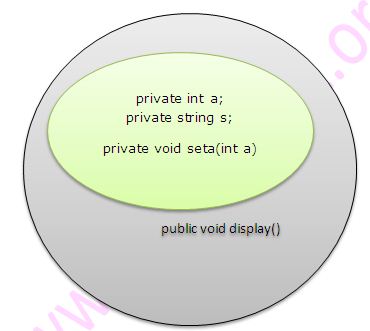 Below example illustrates how encapsulation works in Java.
Below example illustrates how encapsulation works in Java.
 Below example illustrates how encapsulation works in Java.
Below example illustrates how encapsulation works in Java.
package encapsulation;
/**
* Created by ssalunke on 19/04/2016.
*/
public class Encapsulation {
public static void main(String [] args){
A a1 = new A();
//We can not access private members from here
//Below line will throw compilation error saying a has private access
//a1.a
//Below line will throw compilation error saying seta has private access
//a1.seta(1)
//We can access public members from outside of class
a1.display();
}
}
class A{
private int a;
private String s;
private void seta(int a){
this.a = a;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("Display");
}
}
Display
Web development and Automation testing
solutions delivered!!