Java Tutorial
IntroductionEnvironment SetupIDEBuild ManagementLanguage SpecificationBasic ProgramVariablesData TypesPackagesModifiersConditionalsLoopsObject OrientedClassesSuperInterfacesEnumStatic importInheritanceAbstractionEncapsulationPolymorphismBoxing & UnboxingConversion Formatting numbers Arrays Command line arguments in java Variable Number of arguments in Java Exception handling in Java String handling in Java StringBuffer and StringBuilder in Java Mathematical Operations in Java Date and Time in Java Regular expressions in Java Input output programming in Java File Handling Nested Classes Collections Generics Serialization Socket programming Multi-Threading Annotations Lambda Expressions Reflections in Java Singleton class in Java Runtime Class in JavaHow to load resource in JavaHow to load properties file in JavaAdvanced
Log4j – Logging framework in JavaInterview Questions in JavaArrays are used to store similar types of elements in sequential manner. Arrays are fixed in size. You can not grow or shrink the size of array once initialized. Example –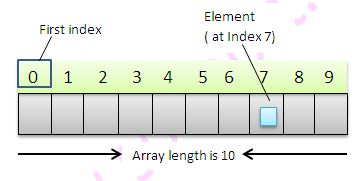
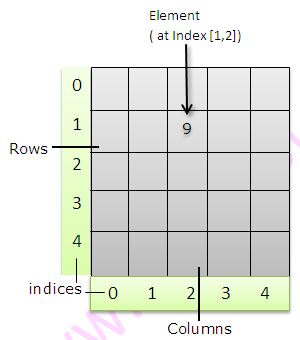 Below example explains how to use arrays in Java.
Below example explains how to use arrays in Java.
int [] a = {11,22,33}
Student [] studentArray = {s1,s2,s3}
- Single Dimensional
- 2-Dimensional
- Multi-dimensional
Single dimensional Array

Two dimensional Array
 Below example explains how to use arrays in Java.
Below example explains how to use arrays in Java.
package arrays;
/**
* Created by ssalunke on 18/04/2016.
*/
public class Array {
public static void main(String [] args){
System.out.println("Let us learn One dimensional array");
int[] primitiveIntArray = new int[3];
int[] primitiveInitializedIntArray = {1,2,3};
int[] primitiveInitializedIntArray1 = new int[]{1,2,3};
//Just like primitives, we can store the reference
// types of objects in Arrays
Student s1 = new Student("s1");
Student s2 = new Student("s2");
Student s3 = new Student("s3");
Student[] studentArray = new Student[3];
Student[] studentInitializedIntArray = {s1,s2,s3};
Student[] studentInitializedIntArray1 = new Student[]{s1,s2,s3};
//Accessing elements in array by using for loop
for(int i=0;i<=2;i++){
System.out.println("Integer Array -> "
+ primitiveInitializedIntArray[i]);
System.out.println("Student Array -> "
+ studentInitializedIntArray[i]);
}
//Accessing elements in array using another variation of for loop
for(int e: primitiveInitializedIntArray){
System.out.println("Integer Array -> " + e );
}
for(Student e: studentInitializedIntArray){
System.out.println("Student Array -> " + e );
}
//***************************************************************//
//Learning 2 dimensional arrays
int [][] twoDimensionalIntArray = new int[3][3];
for(int i=0;i<=2;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=2;j++)
{
twoDimensionalIntArray[i][j] = i+j;
}
for(int[] e: twoDimensionalIntArray){
for(int j:e)
System.out.println("2-D Integer Array -> " + j);
}
//Array of Arrays in Java
int[][] intArrayOfArray =
{primitiveInitializedIntArray,primitiveInitializedIntArray1};
int[][][] intArrayOf2DArray =
{twoDimensionalIntArray,twoDimensionalIntArray};
System.out.println("1st Element in intArrayOfArray -> "
+ intArrayOfArray[0][0]);
System.out.println("1st Element in intArrayOf2DArray -> "
+ intArrayOf2DArray[0][0][0]);
}
}
class Student{
String name;
Student(String s){
this.name = s;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return this.name;
}
}
Let us learn One dimensional array
Integer Array -> 1
Student Array -> s1
Integer Array -> 2
Student Array -> s2
Integer Array -> 3
Student Array -> s3
Integer Array -> 1
Integer Array -> 2
Integer Array -> 3
Student Array -> s1
Student Array -> s2
Student Array -> s3
2-D Integer Array -> 0
2-D Integer Array -> 1
2-D Integer Array -> 2
2-D Integer Array -> 1
2-D Integer Array -> 2
2-D Integer Array -> 3
2-D Integer Array -> 2
2-D Integer Array -> 3
2-D Integer Array -> 4
1st Element in intArrayOfArray -> 1
1st Element in intArrayOf2DArray -> 0
Web development and Automation testing
solutions delivered!!