Basic Linux Tutorial
Introduction – What is it? Why to learn? Linux installation directory structures Boot process Run levels in Linux Desktop Environments Different shells BASH Internal and External Commands Basic Linux Commands Important files and directories in Linux Environmental and Shell Variables Command history in Linux Character classes in Linux Text editors vim nano Searching files Creating new files Viewing File Contents File commands File permissions and ownership WildCards (Globbing) in files File compression Directory commands xargs command in Linux Comparing files Searching patterns using grep command Translating the characters using tr command Extracting data using cut command Stream editing using sed command Data extraction and reporting using awk command Sorting the file or string input uniq command in Linux Difference between grep, tr, cut, sed and awk commands Hardware commands Hard disk and memory space commands Working with Processes Managing Jobs Working with cron jobs Service command in Linux Network commands Managing Users and Groups Other Popular commands Standard streams and Redirection Pipes Package Managers in LinuxNetwork commands in linux shell
Network commands are very helpful in getting information on network interfaces, IP addresses, physical addresses, network connections, domain look up and troubleshooting network issues. Here is the list of network commands in Linux.curl command in Linux
curl command allows you to work with applications using HTTP, FTP, FTPS, HTTPS, SCP, SFTP, TFTP, TELNET, DICT, LDAP, LDAPS, FILE, POP3, IMAP, SMTP, RTMP and RTSP protocols. For example – If you want to download any file from the web server, you can use below command.
$ curl www.softpost.org
$ sudo apt-get install curl
$ curl www.softpost.org -> This command will download the home page of www.softpost.org and display it on standard output.
$ curl -o index.html www.softpost.org -> If you want to save the file instead of viewing it on console, you can use -o option and provide the file name where you want to save downloaded file. Here -o stands for output.
$ curl -O www.example.com/example.html -> If you want to save the downloaded file with same name as url, you can use -O option.
$ curl https://securesite.com/login.html
$ curl –insecure https://self-signed-cert.com/login.html
wget command in Linux
wget command is just like curl. Main difference is that wget command supports only HTTP, HTTPS and FTP protocols. Also curl is more widely used than wget. wget can get the urls recursively. Here is the list of wget commands.
$ wget www.softpost.org -> This command will download the home page of www.softpost.org and display it on standard output.
$ wget -o index.html www.softpost.org -> If you want to save the file instead of viewing it on console, you can use -o option and provide the file name where you want to save downloaded file. Here -o stands for output.
$ wget ‐‐input url-list.txt -> This command can be used to download multiple urls specified in url-list.txt file.
ping command in Linux
ping command is used to check the connection with other host
$ ping <host-name>
$ ping -c 4 <host-name>
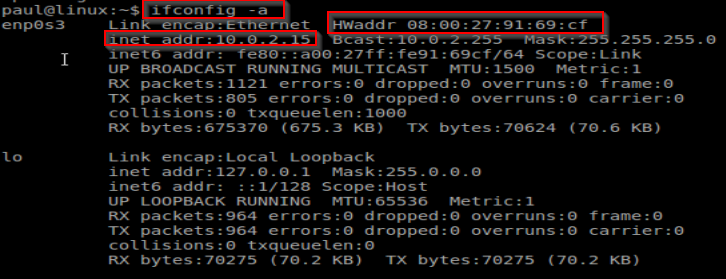
ifconfig command in Linux
ifconfig command shows the ip address and physical address of each network interface on the host.
$ ifconfig -a
hostname command in Linux
$ hostname
# This command can be used to print or set system name.
$ hostname <new-host-name>
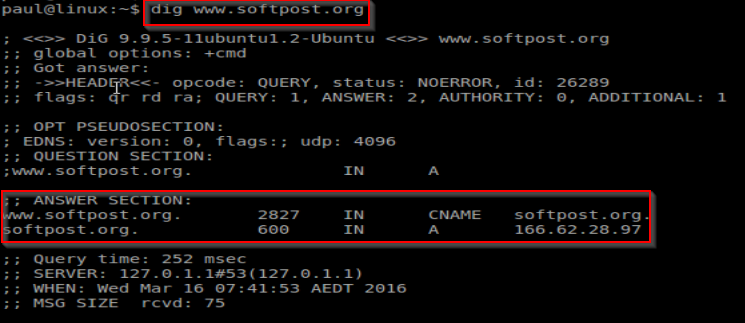
dig/host/nslookup command in Linux
dig command is used for getting DNS information of domain name
$ dig www.softpost.org
 host and nslookup commands also provide similar information.
host and nslookup commands also provide similar information.traceroute command in Linux
traceroute command is used to trace the route to Host.
$ traceroute www.softpost.org
$ sudo apt-get install traceroute
netstat command in Linux
netstat stands for network statistics. This command shows all network connections as well as network interface information. To know about all tcp and udp connections, you can use below command. Here -t stands for TCP connection. -u stands for UDP connections.
$ netstat -tu
$ netstat -a
lsof command in Linux
Below command can be used to display the list of all open files including the ones used by network connections.
$ sudo lsof
$ lsof -i tcp
$ lsof -i udp
lsof -i :80
ftp command in Linux
ftp command allows you to upload, download, manage files on FTP server To connect to any server, type below command.
$ ftp <server-name>
- put filename – Upload a file to the server
- get filename – Download a file from the server
- mput *.txt – Put multiple files ending with .txt on the server
- mget *.txt – Get multiple files ending with .txt from the server
- ls – Get a list of files in the current directory
- cd – Change directory
- quit – Close your ftp session
telnet command in Linux
telnet command can be used to manage the compute remotely. It is less secure as compared to ssh command. Data is transferred in plain text.ssh command in Linux
ssh stands for Secure Shell Protocol. You can remotely login to computer and execute the commands using ssh command. Data is encrypted before transmission. Below command will show ssh version you are using.
$ ssh -V
route/arp command in Linux
route command shows the kernel routing table. Here is the sample output. arp stands for address resolution protocol. arp command shows all ARP entries in the system.
arp stands for address resolution protocol. arp command shows all ARP entries in the system.Web development and Automation testing
solutions delivered!!